The Ekdahl FAR - Bowing jack: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The ''bowing jack'' holds the ''bowing motor'' which in turn has a ''wheel holder'' attached to its shaft. It's this ''wheel holder'' that ultimately holds the ''bowing wheel'' that actually creates sounds by rubbing against the string. | The ''bowing jack'' holds the ''bowing motor'' which in turn has a ''wheel holder'' attached to its shaft. It's this ''wheel holder'' that ultimately holds the ''bowing wheel'' that actually creates sounds by rubbing against the string. | ||
The ''wheel holder'' is painted half black and half white, this is because underneath it is a ''reflection sensor'' which is responsible for measuring the speed of the ''bowing motor'' which is <u>crucial</u> | The ''wheel holder'' is painted half black and half white, this is because underneath it is a ''reflection sensor'' which is responsible for measuring the speed of the ''bowing motor'' which is <u>crucial</u> for the motor to bow the right frequencies. The Ekdahl FAR comes with a ''bow cover'', the reason to use this cover is not only to protect the ''bowing jack'' but also to block out ambient light since strong light can interfere with the ''reflection sensor''. | ||
The entire ''bowing jack'' is riding on an ''axle bolt'' so that it can move up and down. Below the ''bowing jack'' to the side is the ''pressure motor'', this has a ''corkscrew'' attached to its output shaft which is responsible for pushing the ''bowing jack'' up and down. Through this mechanism the ''bowing wheel'' can be moved ~4mm / 3/16" up and down by sending the instruments the various ''pressure''-commands. | The entire ''bowing jack'' is riding on an ''axle bolt'' so that it can move up and down. Below the ''bowing jack'' to the side is the ''pressure motor'', this has a ''corkscrew'' attached to its output shaft which is responsible for pushing the ''bowing jack'' up and down. Through this mechanism the ''bowing wheel'' can be moved ~4mm / 3/16" up and down by sending the instruments the various ''pressure''-commands. | ||
Revision as of 23:33, 23 January 2025
Overview
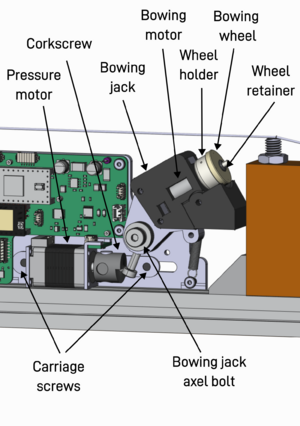
The bowing jack is one of the most important parts of the Ekdahl FAR as it holds the bowing motor which is what ultimately controls what harmonics are being emphasized by the instrument. It also sets the volume and harmonic content by regulating the pressure of the bowing wheel against the string.
The bowing jack may at times have to be adjusted when changing to a different string or attempting to use differently sized bowing wheels.
Mechanical details
The bowing jack holds the bowing motor which in turn has a wheel holder attached to its shaft. It's this wheel holder that ultimately holds the bowing wheel that actually creates sounds by rubbing against the string.
The wheel holder is painted half black and half white, this is because underneath it is a reflection sensor which is responsible for measuring the speed of the bowing motor which is crucial for the motor to bow the right frequencies. The Ekdahl FAR comes with a bow cover, the reason to use this cover is not only to protect the bowing jack but also to block out ambient light since strong light can interfere with the reflection sensor.
The entire bowing jack is riding on an axle bolt so that it can move up and down. Below the bowing jack to the side is the pressure motor, this has a corkscrew attached to its output shaft which is responsible for pushing the bowing jack up and down. Through this mechanism the bowing wheel can be moved ~4mm / 3/16" up and down by sending the instruments the various pressure-commands.
Adjusting the bowing jack
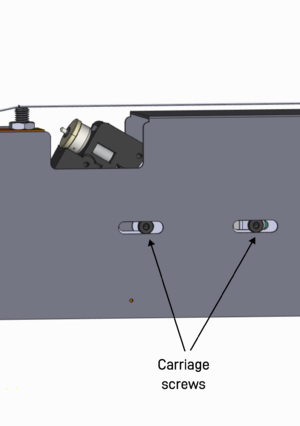
At times the bowing jack will need to be adjusted, this could be because the bowing wheel cannot reach the full pressure wanted or because the bowing wheel is still touching the string when in the rest position. The pressure motor can be moved so that the range of the bowing jacks movements comprises the entire range of the bowing wheel not touching the string, to it being pressed into the string hard enough to create a full sound. Before moving the pressure motor the user needs to make sure that the bridges are placed in the right position and that the movements of the bowing jack aren't simply hampered by the current calibrations.
Before moving the pressure motor you should start by putting the bowing jack in its lowest position, you can use the configuration utility and click the Reset pressure rest and go to pressure rest position-button under the Advanced-tab. This will set the bow pressure rest position to zero and tell the bowing jack to go to the bow pressure rest position. If the shield is taken off of the Ekdahl FAR you can instead - while the unit is off - rotate the corkscrew that controls the position of the bowing jack to its lowest position.
The pressure motor is fastened with two carriage screws, these can be accessed without removing the shield by using the long end of a 3mm hex key. Carefully loosen the screws just enough so that you can slide the carriage, by not removing the hex key from the last screw head you can use it to carefully slide the pressure motor without removing the shield. As a rule of thumb, the bowing wheel should be ~1mm below the string at its lowest position. Remember that different wheels have different pressure properties, a new completely round wheel is generally a good reference candidate. Using the latter when you set the pressure motors position, most other bowing wheels should be able to have a full reach without having to move the pressure motor again.